Security Services & Framework
Octree's Integrated Cyber Security Proposition, the Securapro Framework maps directly to NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) Cyber Security Framework 2.0, and provides a comprehensive cyber security management program addressing People, Processes and Technology.
By adopting a cybersecurity framework, your organization can establish a robust, comprehensive approach to security that addresses current threats and prepares you for future challenges. It's an essential step in safeguarding your digital assets and maintaining the trust of your stakeholders in an increasingly connected world.
A cyber security framework can be used by organizations to understand, assess, prioritize, and communicate cybersecurity risks; it is particularly useful for fostering internal and external communication across teams — as well as integrating with broader risk management strategies.
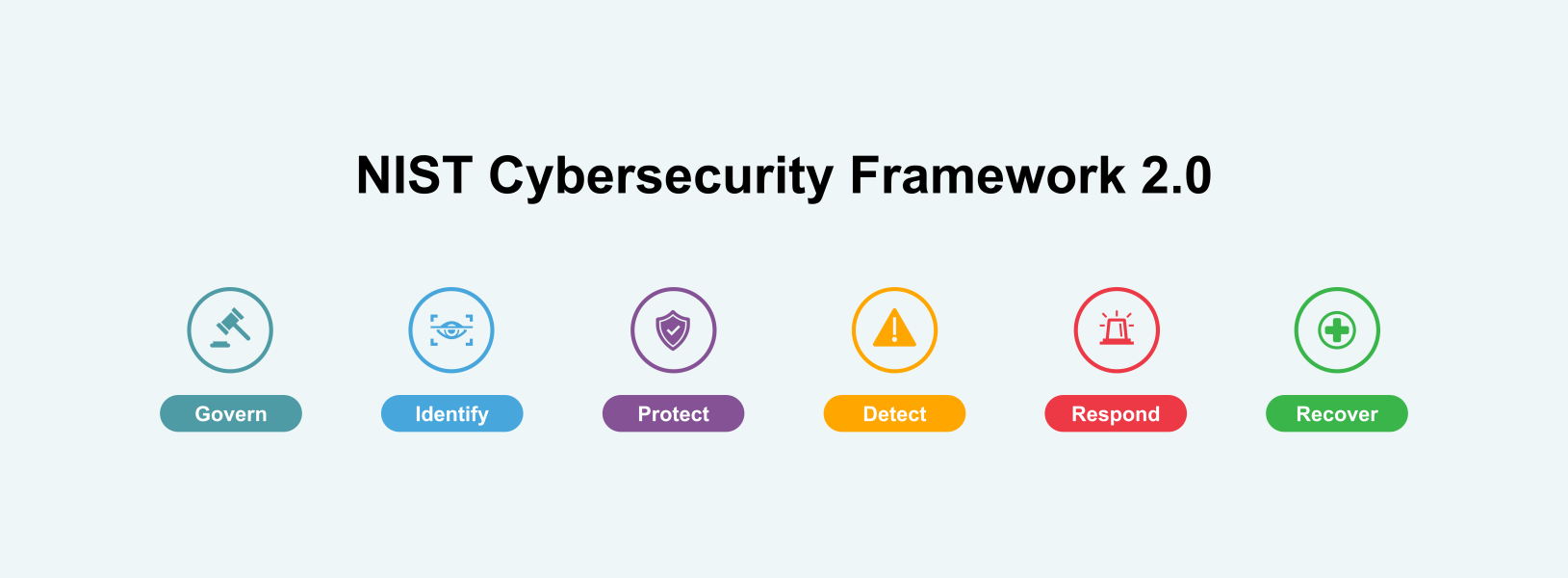
Identify: The organization’s current cybersecurity risks are understood
The Identify function is crucial for developing an organizational understanding of cybersecurity risks to systems, assets, data, and capabilities. It involves activities such as asset management, business environment analysis, governance, risk assessment, and risk management strategy development. This function helps organizations establish the context required for effective cybersecurity risk management decisions.
Protect: Safeguards to manage the organization’s cybersecurity risks are used.
The Protect function is designed to develop and implement appropriate safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services. It supports the ability to limit or contain the impact of potential cybersecurity events. This function encompasses activities like access control, awareness and training, data security, information protection processes and procedures, maintenance, and protective technology implementation.
Detect: Possible cybersecurity attacks and compromises are found and analyzed
The Detect function enables the timely discovery of cybersecurity events. It involves developing and implementing appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of cybersecurity incidents. This function includes categories such as anomalies and events detection, security continuous monitoring, and detection processes. Effective detection capabilities are crucial for rapid response to potential threats.
Respond: Actions regarding a detected cybersecurity incident are taken.
The Respond function focuses on developing and implementing appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident. It supports the ability to contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity event. This function includes response planning, communications, analysis, mitigation, and improvements. A well-prepared response can significantly reduce the impact of cybersecurity incidents on an organization.
Recover: Assets and operations affected by a cybersecurity incident are restored.
The Recover function aims to develop and implement appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity event. This function supports timely recovery to normal operations to reduce the impact of a cybersecurity incident. It includes activities such as recovery planning, improvements, and communications. Effective recovery processes ensure that organizations can quickly return to normal operations after an incident, minimizing disruption and potential losses.
Govern: The organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy, expectations, and policy are established, communicated, and monitored.
This function emphasizes the importance of cybersecurity governance within an organization. It focuses on establishing and maintaining the governance structures necessary to manage cybersecurity risks in alignment with business objectives and regulatory requirements. The Govern function includes activities such as defining organizational context, developing risk management strategies, assigning roles and responsibilities, creating policies, providing oversight, and managing cybersecurity supply chain risks.
Fixed cost, flexible plans, great IT support.
To find out more about how we can resolve your IT issues please email or call us:
Send us an email Call us +44 (0)1462 416400















